The methanol synthesis and distillation
The formation of green methanol
The methanol synthesis and distillation
The formation of green methanol
The methanol synthesis and distillation
The formation of green methanol
The production of green methanol - the fuel of the future
Methanol is already known as a fossil fuel and is used in a wide variety of areas for a wide variety of things. However, it can be produced in many different ways; some sustainable, others not. Green methanol synthesis is one of the newest methods of obtaining methanol and the most sustainable of all. It usesCO2 captured from industry to produce methanol in a sustainable, emission-free and environmentally friendly way.
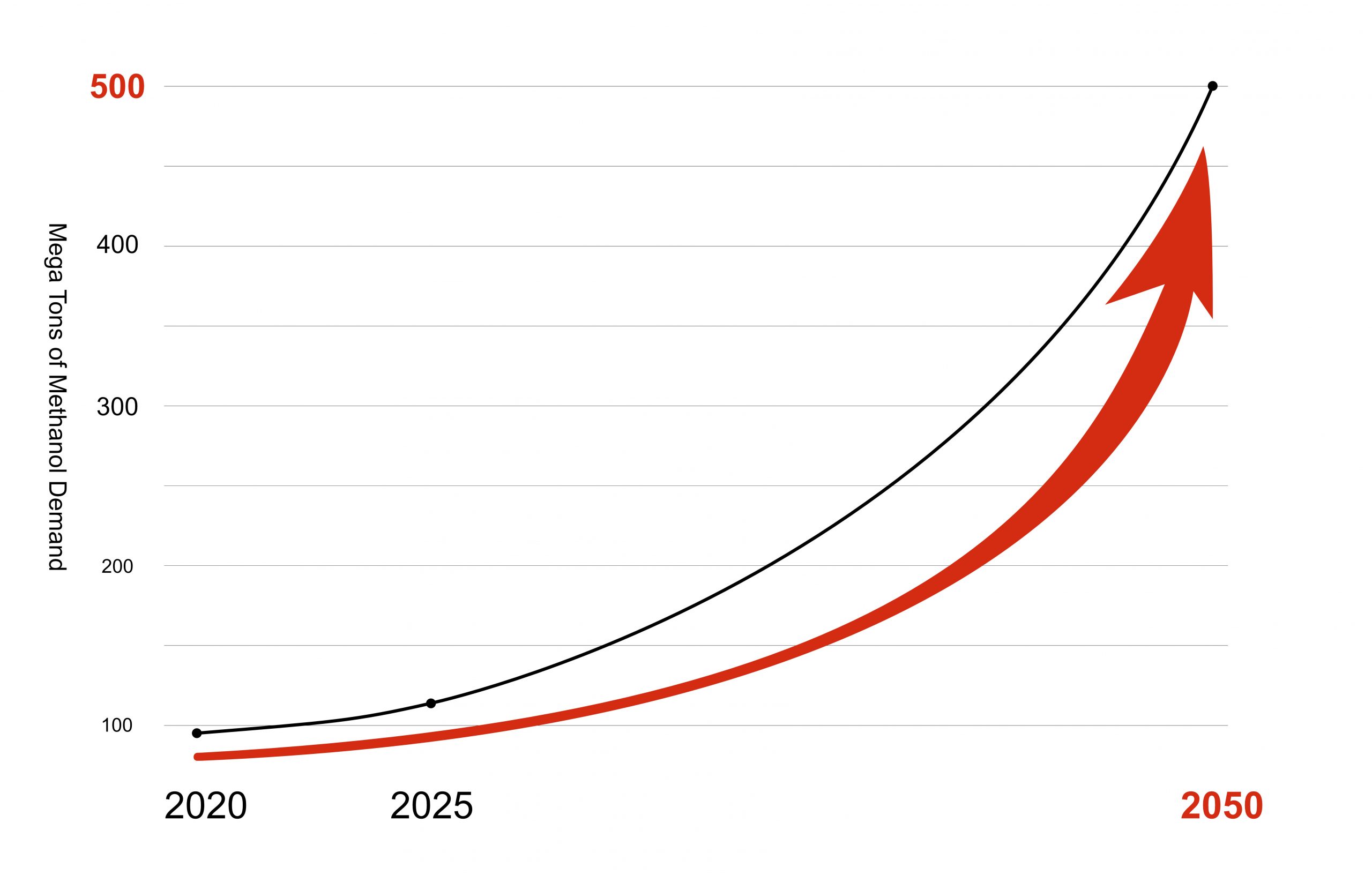
Data Source: Innovation Outlook : Renewable Methanol- IRENA
The production of green methanol - the fuel of the future

Data Source: Innovation Outlook : Renewable Methanol - IRENA
Methanol is already known as a fossil fuel and is used in a wide variety of areas for a wide variety of things. However, it can be produced in many different ways; some sustainable, others not. Green methanol synthesis is one of the newest methods of obtaining methanol and the most sustainable of all. It usesCO2 captured from industry to produce methanol in a sustainable, emission-free and environmentally friendly way.

Why do we need green methanol?
Global demand for methanol is high and rising with increasingCO2 taxes, increasingly polluted air and ever more ambitious climate targets. So far, however, most methanol is not produced sustainably, although there is already a solution. The solution consists of 2 steps: methanol synthesis from recycledCO2 followed by distillation.
Why do we need green methanol?

Global demand for methanol is high and rising with increasingCO2 taxes, increasingly polluted air and ever more ambitious climate targets. So far, however, most methanol is not produced sustainably, although there is already a solution. The solution consists of 2 steps: methanol synthesis from recycledCO2 followed by distillation.
How does methanol synthesis work?
Initially, carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen (H2) are needed. Both can be produced emission-free (by electrolysis using CSP-PV hybrid power plants) or even emission-preventing (byCO2 capture). The two substances are processed under a pressure of 40 bar and at a temperature of 240°C.CO2 and H2 are mixed in the correct ratio, with theCO2 as a variable stream adjusted to the actual hydrogen stream. The temperature of the gas stream is adjusted to the optimum operating temperature of the methanol catalyst (about 240°C) using heat exchangers. The heated gas flows in the fixed-bed reactor from top to bottom through tubes filled with a catalyst. This catalyst (Cu/ZnO/Al2O3) was developed for exactly this purpose.
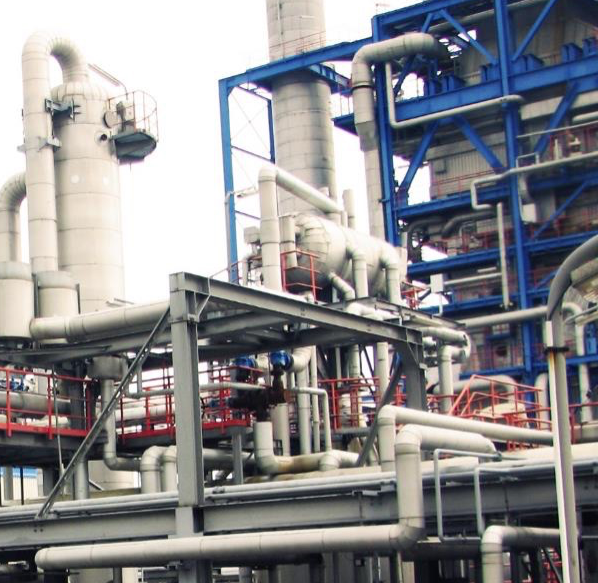

Finally, the crude methanol, consisting mainly of methanol, water and small amounts of by-products, is stored in a buffer tank, which serves as a feed for the methanol distillation to achieve IMPCA specifications (methanol purity > 99.85 wt%). The heat of reaction from the exothermicCO2 hydrogenation is used to generate steam, which is used internally to partially meet the heat demand of the methanol distillation. The partially converted syngas leaves the reactor and is cooled to 80°C in a gas/gas heat exchanger. The raw methanol is then condensed and separated from the unreacted synthesis gas, which is returned to the reactor via the recycle gas compressor.
How does methanol synthesis work?

Initially, carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen (H2) are needed. Both can be produced emission-free (by electrolysis using CSP-PV hybrid power plants) or even emission-preventing (byCO2 capture). The two substances are processed under a pressure of 40 bar and at a temperature of 240°C.CO2 and H2 are mixed in the correct ratio, with theCO2 as a variable stream adjusted to the actual hydrogen stream. The temperature of the gas stream is adjusted to the optimum operating temperature of the methanol catalyst (about 240°C) using heat exchangers. The heated gas flows in the fixed-bed reactor from top to bottom through tubes filled with a catalyst. This catalyst (Cu/ZnO/Al2O3) was developed for exactly this purpose.
Finally, the crude methanol, consisting mainly of methanol, water and small amounts of by-products, is stored in a buffer tank, which serves as a feed for the methanol distillation to achieve IMPCA specifications (methanol purity > 99.85 wt%). The heat of reaction from the exothermicCO2 hydrogenation is used to generate steam, which is used internally to partially meet the heat demand of the methanol distillation. The partially converted syngas leaves the reactor and is cooled to 80°C in a gas/gas heat exchanger. The raw methanol is then condensed and separated from the unreacted synthesis gas, which is returned to the reactor via the recycle gas compressor.